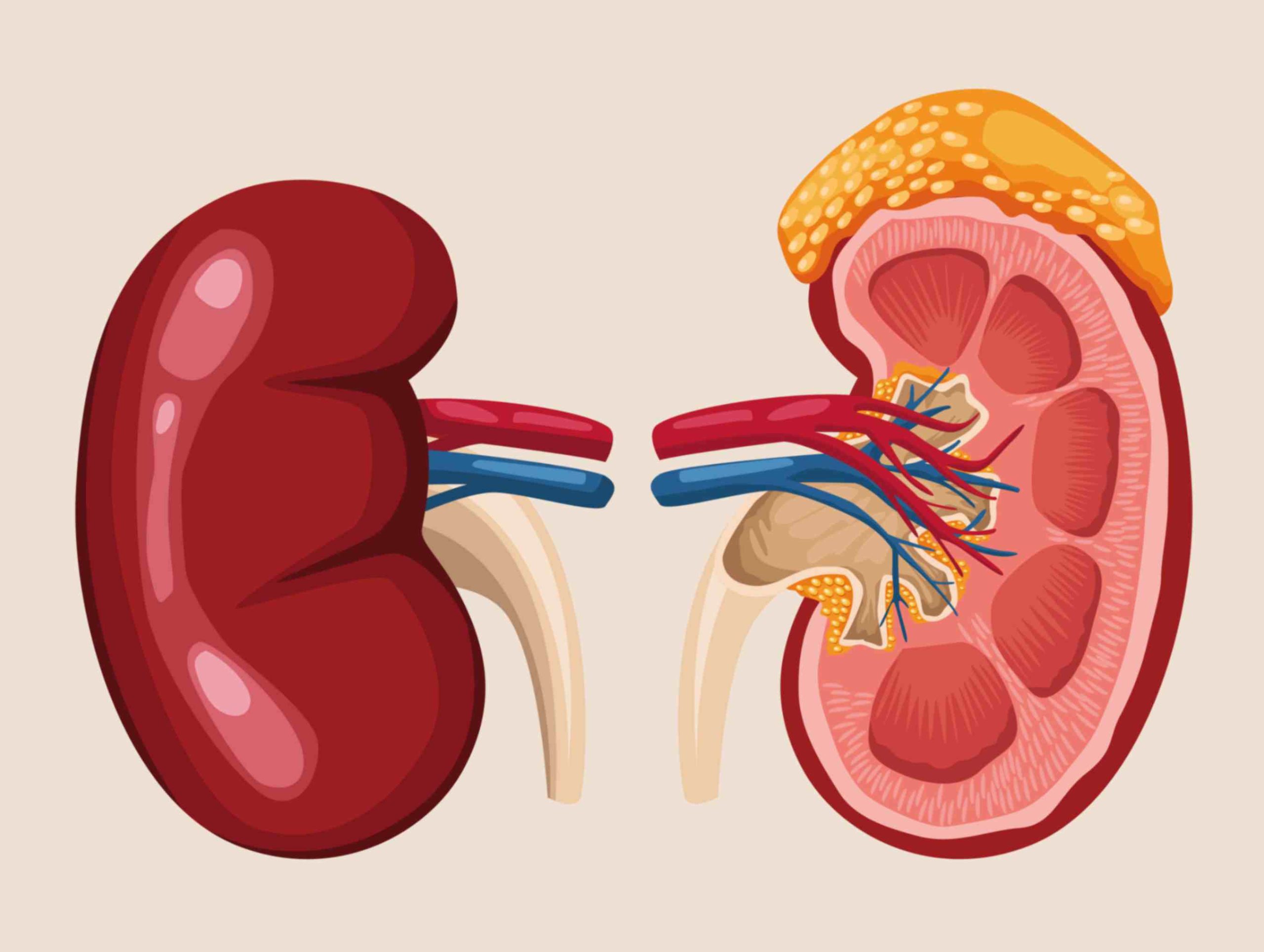
Nephrology
Nephrology is a specialty that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of kidney disorders. Though it focuses on primary kidney disorders, the department of nephrology maintains expertise in managing the systemic consequences that arise due to impaired kidney functionality. It also takes the responsibility to prevent the conditions that cause renal (kidney) damage.
With extensive experience, the Nephrologist at Optimus Super Speciality Hospital is highly skilled to treat chronic kidney diseases. Our Nephrologist is trained and also work with other Pediatric specialists to diagnose and treat kidney disorders in children and adolescents along with adults. A multidisciplinary team of nurses, dieticians, and technical staff work with the nephrologists to create a patient-centric environment and provide high-quality care for patients with kidney dysfunctionalities.
Nephrology services at Optimus Super Speciality Hospital, where our commitment to excellence is reflected in a Advanced facility designed to provide comprehensive and advanced care for renal health.
Optimus Super Speciality Hospital है तो सब मुमकिन है।
Advanced Diagnostic Services
Our nephrology department is equipped with highly Advanced diagnostic tools, including advanced imaging modalities such as ultrasound, CT scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These technologies enable precise and early detection of kidney diseases, allowing our experts to tailor treatment plans effectively.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), formerly known as acute renal failure, refers to a sudden and rapid decline in kidney function. While most cases are managed medically, surgical intervention becomes necessary in specific situations where conservative approaches prove insufficient. Encompasses the abrupt impairment of renal function, leading to a compromised capacity for blood filtration. Clinical manifestations of acute kidney injury encompass dyspnea, fatigue, cognitive disorientation, lower extremity oedema, and nausea.
Severity of Acute Kidney Injury
- Clinical Stages: AKI is categorized into three clinical stages based on serum creatinine levels and urine output. The severity progresses from Stage 1 (mild) to Stage 3 (severe).
- Potential Complications: Severe AKI can lead to life-threatening complications such as electrolyte imbalances, fluid overload, and metabolic acidosis. These complications underscore the importance of timely medical evaluation.
Signs and Symptoms of AKI
- Decreased Urine Output: A significant reduction in urine output, known as oliguria, may indicate advanced stages of AKI. Anuria, where no urine is produced, is a critical sign requiring urgent attention.
- Fluid Retention: Noticeable swelling in the extremities, face, or abdomen due to fluid retention can be indicative of worsening kidney function and necessitates prompt medical assessment.
- Symptoms of Uraemia: As AKI progresses, symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, confusion, and seizures may arise, indicating a critical stage requiring immediate medical intervention.
Urgent Situations Requiring Medical Attention:
- Sudden Onset: If AKI develops suddenly, especially following trauma, severe infections, or exposure to nephrotoxic substances, immediate medical attention is imperative to determine the underlying cause and initiate appropriate interventions.
- Severe Dehydration: Conditions leading to severe dehydration, such as persistent vomiting, diarrhoea, or excessive fluid loss, can trigger AKI. In such cases, seeking medical help promptly is crucial to prevent further renal damage.
- Medication-Induced AKI: Certain medications and contrast agents can precipitate AKI. If an individual experiences a rapid decline in kidney function after medication use, seeking immediate medical advice is essential.
Kidney Stone Treatment
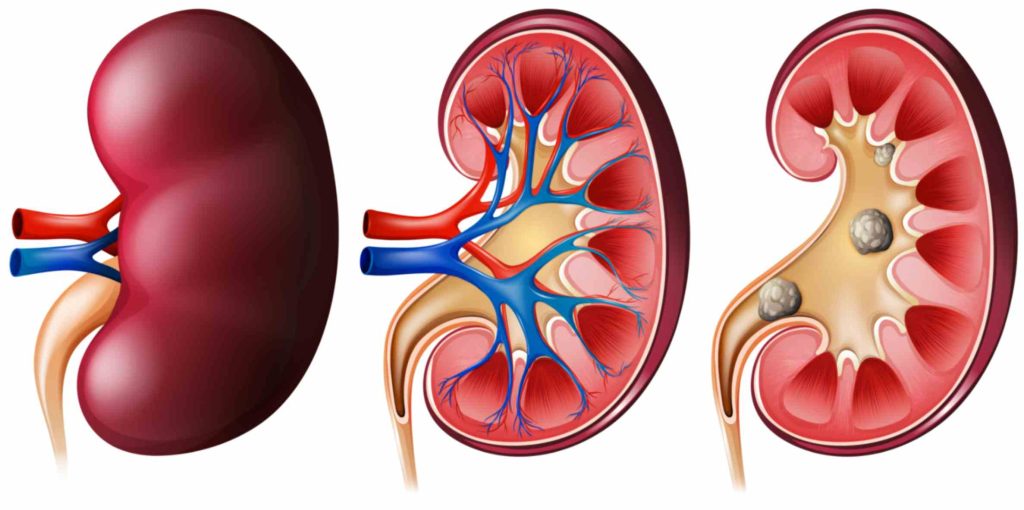
Kidney stone surgery involves intricate procedures aimed at the removal of kidney stones that prove too large to pass naturally cause severe pain, infections, or hinder kidney function. Under the purview of a urologist – a specialist in urinary tract diseases – various surgical approaches are employed based on factors such as stone size, location, and patient preference.
Kidney stones, also known as renal calculi, are solid deposits of minerals and salts that form within the kidneys or urinary tract. They can cause severe pain, discomfort, and complications if not properly managed. Understanding the treatment options and management strategies for kidney stones is crucial for effective relief and prevention of recurrence.
Diagnosis and Tests:
1. Imaging Tests:
Upon suspicion of kidney stones, your healthcare provider initiates a diagnostic process involving a thorough discussion of your medical history and the prescription of specific tests. Advanced imaging techniques, including X-ray, CT scan, and ultrasound, are deployed to precisely visualize the size, shape, location, and quantity of kidney stones. These critical insights inform the provider’s decision-making regarding the appropriate treatment strategy.
2. Blood Test:
A comprehensive blood test is conducted to assess the renal functionality, identify potential infections, and detect biochemical irregularities that may contribute to the development of kidney stones. This diagnostic step provides essential information about the overall health of the kidneys.
3. Urine Test:
Analysis of urine samples is undertaken to identify signs of infection and scrutinize the levels of substances implicated in the formation of kidney stones. This thorough examination aids in obtaining a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s renal condition.